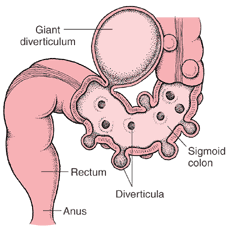
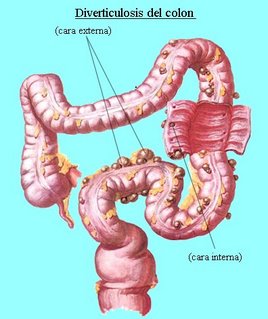
Deverticulosis is the condition in which an individual has multiple diverticulae. A Diverticulum is a douch or sac in the walls of a canal or an organ.
Diverticulosis usually occurs in about 10 % of individuals over 40 years of age and nearly 50 % of person over age 60; only small percentage develop diverticulitis.
The condition is most common in sigmoid colon. Small bowel diverticula are unsual, but when they occur, they are multiple. They may act as areas of statis and bacterial overgrowth, leading to malabsorption of fat and vitamin B12.
If the diverticulum perforates, local abcess or peritonitis results.
Predisposing Factors :a. Probable congenital predisposition.
b. Weakening and degeneration of muscular wall of the intestine, causing herniation of the lining of the mucous membrane through a muscle.
c. Chronic overdistention of the large bowel.
d. Diet low in roughage-reduce and fecal residue, narrows the bowel lumenand leads to higher pressure intra abdominally during defecation.
Specific Clinical Signsa. Diverticulosis :
- Bowel irregularity
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Sudden massive hemorrhage
b. Milder form of Diverticulitis :
- Mild lower abdominal cramps
- Bowel irregularity, constipation and diarrhea
- Mild nausea, gas, low grade fever and leukocytosis
c. Moderatly severa acute Diverticulitis :
- Crampy pain in lower left quadrant of abdomen
- Low grade fever, chill and leukocytosis
- Ruptured diverticulum produces abscess, ruptured diverticulum near a blood vessel may cause massive hommorhage.
d. Chronic diverticulitis may cause adhesions that narrow the bowels opening and can partial or complete bowel obstruction.
 DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION1.
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION1. History, physical examination, laboratory evaluation
2. Flat film of abdomen
3. Ultrasonography, CT-Scan
4. Sigmoidoscopy; possibly colonoscopy
5. Barium Enema (After Infection Subsides)
Surgical Management :If there is little response to medical treatment or if complications such as hemorrhage, obstructions or perforation occurs, surgery is necessary.
Hemorrhage may require transfusion if hemorrhage is life threatening, total collection is with ileostomy and preservation of rectal stump may be required. Continuity of the bowel is reestablished subsequently.
Intestinal obstruction /perforations-temporary colostomy is sometimes performed to divert fecal stream.
Nursing Care Analysis :
1.a. Nursing Diagnosis
Pain Related to intestinal discomfort, diarrhea and/or constipation
b. Objectives
Patient will have tolerable pain/absence of pain
c.Nursing Intervention
· Assess pts condition
· Observe for sign and location of pain, type and severity
· Auscultative for bowel sounds
· Palpate abdomen to determine rigidity or tenderness due to perforation or peritonitis
· Administer analgesia as prescribed or anti cholinergic as prescribed to decrease colon spasm.
d.Evaluation
Patient expressed relief of pain and has a decrease in symptoms.
2. a.Nursing Diagnosis
Altered nutrition less than body requirements related to diarrhea, fluid and electrolyte loss, nausea and vomiting
b. Objectives
To maintain adequate nutrition· Follow prescribed diet that is high in fat residue low in sugar
c. Nursing Intervention
· Encourage increase fluid intake
· Regulate IVF properly in case of NPO
· Monitor intake output
d. Evaluation
Consumes prescribed diet and can relate what foods to include or avoid
3. a. Nursing Diagnosis
Altered bowel elimination related to disease process
b. Objectives
Promoting normal bowel elimination
c. Nursing Intervention
· Advise patient to establish regular bowel habits to promote regular and complete evacuation
· Observe color, consistency and frequency of stool and record
· Encourage fluids if constipated
· Provide soft, high residue, low roughage, low sugar diet to provide bulk; more consistency to the stool.
d.Evaluation
Reports near normal bowel function; no diarrhea or constipation.
4. a. Nursing Diagnosis
Knowledge deficit of the relation between diet and diverticulosis
b. Objective
To Increase understanding
c. Nursing Intervention
· Explain the disease process to the patient its relationship to diet
· Have the patient continue periodic medical supervision and follow up; report problem and untoward symptoms
d.Evaluation
Incinerates the general nature of diverticulosis and can list what helps or aggravates the condition
Read more here............